With the rapidly increasing institutional adoption of digital assets, financial organizations need secure and efficient ways to scale and operate to capitalize on growing demand.
Today, multi-sig and MPC are two of the most common technologies for securing private keys. You may be wondering – which is a better option for my organization?
In this blog post, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know about both technologies so you can get a better sense of which fits your organization’s needs.
The multi-sig challenge
Multi-sig (multi-signature) is a digital signing process that enables two or more users to sign transactions as a group.
Before multi-sig wallets entered the mainstream, cryptocurrencies were generally stored using a single private key. Whoever had access to the private key itself was able to access the funds associated with that key. Multi-sig added an additional layer of security to the equation by creating wallets that require the signature from multiple keys.
While multi-sig offers potential solutions to some of the problems of single-signature wallets, it also introduces new issues. This is because when multi-sig was first introduced in 2012, the blockchain space was different in a variety of ways. For example, bitcoin was the only cryptocurrency, so the concept of creating a security technology that would work across multiple blockchains was irrelevant.
In today’s fast-paced digital asset landscape, multi-sig-based solutions can no longer support the needs of a digital asset business because:
Multi-sig is not protocol agnostic
Not all cryptocurrency protocols support multi-sig – and those who do have very different implementations from one another. This makes it more difficult for multi-sig wallet providers to securely support new chains.
With an on-chain multi-sig solution, each protocol requires the wallet provider to implement a different code. When a multi-sig implementation goes wrong, various issues can arise:
- The Multi-sig Parity Wallet – Poor implementation lead malicious actors to steal around $30m worth of Ethereum in one of the biggest wallet hacks to date.
- Parity Wallet Hacked (Again) – A hacker again gained access to the wallet and froze $300m worth of Ethereum. Some customers lost up to $300k worth of digital assets.
- Vulnerabilities in Bitcoin Multi-sig – Discovered by the Fireblocks Research team, a vulnerability in the bitcoin multi-sig check implementation was deployed in development environments and, despite the popularity of this codebase, the vulnerability still remains.
Multi-sig is operationally inflexible
Multi-sig cannot offer the operational flexibility organizations require as they grow. As your team expands, you will need to adjust the process of accessing and transferring your digital assets. This can include changing the number of employees required to sign a transaction, adding new key shares as you hire new employees, revoking key shares as employees leave, and modifying the required threshold to sign transactions (e.g. from ‘3 of 4’ to ‘4 of 8’). In these sorts of scenarios, multi-sig addresses create various obstacles, as they are pre-set to the wallet.
MPC (multi-party computation) has quickly become accepted as the next generation of private key security.
MPC crypto removes the concept of a single private key; such a key is never gathered as a whole, neither during the first creation of the MPC wallet nor during the actual signature. MPC follows a set of steps to guarantee that there is never a single point of compromise of the private key:
- Individual secrets are randomized by each of the several (always more than 3) endpoints – either servers or mobile devices. Those secrets are never shared with each other.
- The individual endpoints engage in a decentralized wallet creation protocol in which they compute the public key (wallet address) that corresponds to the set of individual private shares.
- When a signature on a blockchain transaction is requested, a quorum (at least 3) of endpoints engage in a distributed signature process where each one of the endpoints individually validates the transaction and policy and signs the transaction.
In a similar fashion to multi-sig, the MPC private key protection layer removes the single point of compromise from both external hackers and insiders – as the private key is never concentrated on a single device at any point in time.
Security and risk management: evaluating threats in MPC and multi-sig solutions
When it comes to securing digital assets, multisig wallet solutions and MPC crypto technologies represent two leading approaches to enhanced security. Multi-signature wallets and security protocols offer robust protection by requiring multiple parties to authorize transactions, making them particularly attractive for institutional custody. However, understanding and mitigating potential security risks remains paramount regardless of the chosen solution.
With multi-signature wallets and security measures in place, organizations must primarily guard against vulnerabilities in the blockchain protocol’s multisig implementation and manage the operational complexities of multiple signers. History has shown that flawed implementations can result in catastrophic losses worth millions. This necessitates thorough auditing and testing of any multisig wallet deployment.
MPC crypto technology offers a different security paradigm by never assembling the complete private key in one location. This distributed approach inherently strengthens resilience against both internal threats and external attacks. However, thorough vetting of the MPC provider’s infrastructure, security practices, and access controls remains essential for maintaining robust protection.
Disaster recovery represents another crucial consideration. Traditional multisig wallet setups require careful advance planning for signer management, while MPC crypto solutions typically offer more flexibility in modifying authorized parties. Both approaches significantly enhance security compared to single private key storage, but organizations must carefully evaluate their specific needs and risk profile when choosing between them.
The key to success lies in understanding the distinct threat models associated with each approach and conducting comprehensive due diligence to select the solution that best aligns with organizational requirements. When protecting valuable digital assets, security must remain the foremost priority, whether implementing multisig wallet infrastructure or MPC-based systems.
MPC frees digital asset operations
MPC’s distributed nature allows team members to require multiple authorizers for a transaction and sign transactions without being in the same location. Operationally, it’s a significant advancement over multi-sig due to its inherent flexibility; unlike multi-sig, MPC allows for ongoing modification and maintenance of the signature scheme.
While multi-sig wallets were an important step forward, the limitations of the technology have become increasingly apparent as the ecosystem has evolved. MPC, on the other hand, addresses many of these limitations and provides a more flexible, future-proof solution for securing digital assets. As you evaluate the right approach for your organization, it’s important to carefully consider the tradeoffs and choose the solution that best fits your specific needs and requirements.
MPC vs. multi-sig breakdown
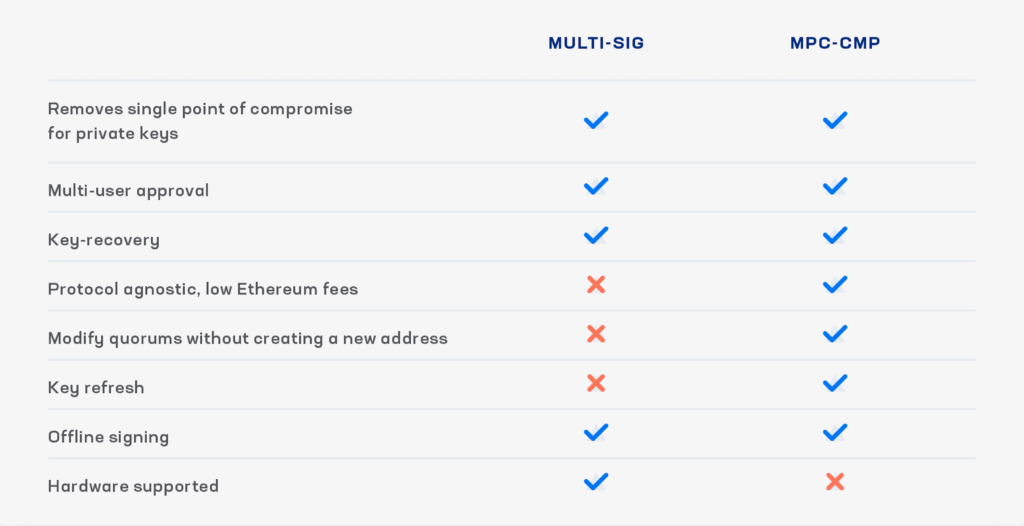
Looking to get more information on how MPC and multi-sig stack up?
- Check out the Ethereum Cost Savings Calculator to learn exactly how much organizations are saving on ETH deposit address management by switching from multi-sig to MPC.
- Download the info sheet to learn more about the differences between MPC-CMP and multi-sig technology.
